Last Updated on September 12, 2025
Key Takeaways
- Cutaneous lupus erythematosus is an autoimmune skin disease that causes rashes, lesions, and sun sensitivity.
- Women aged 20–40 with genetic or environmental risk factors are more likely to develop it.
- Treatment includes sun protection, medications, lifestyle changes, and emotional support.
- Prevention and ongoing research provide hope for better management and future therapies.
When it comes to autoimmune conditions, few are as complex and misunderstood as cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Because the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin tissue, this condition can be both physically uncomfortable and emotionally challenging. However, with the right information, patients and caregivers can better understand what is happening and explore potential strategies for managing symptoms effectively. In this blog post, we will answer the question “what is cutaneous lupus erythematosus?” while also exploring its possible symptoms, causes, and treatment options.
What is Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus?
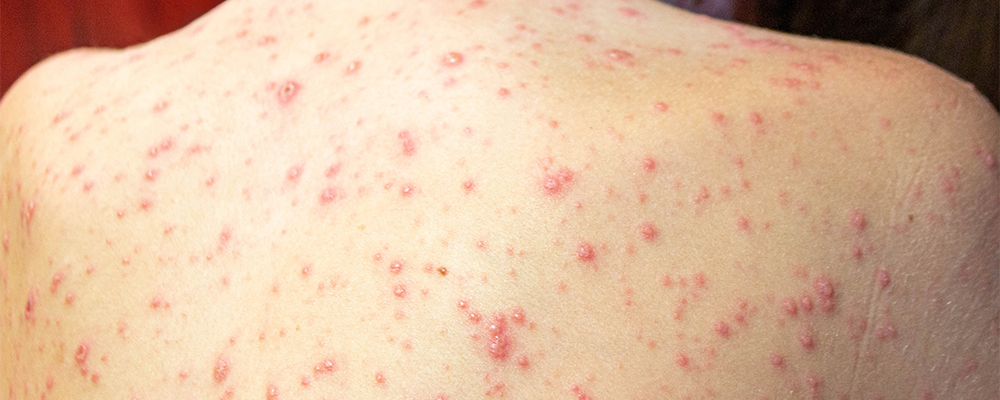
To begin with, cutaneous lupus erythematosus is a chronic autoimmune disease that primarily affects the skin. Unlike systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), which can target multiple organs, this type of lupus usually remains confined to the skin. In other words, the immune system becomes overactive and begins to attack healthy skin cells, resulting in inflammation, rashes, lesions, and sensitivity to sunlight.
Although it is not life-threatening in most cases, the condition can still have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life. For example, patients often struggle with visible skin changes, which may lead to emotional distress or reduced self-confidence. At the same time, the physical discomfort caused by flare-ups, such as burning, itching, or pain, can also interfere with daily activities.
Who is at Risk?
Research suggests that women are more frequently affected than men, and onset often occurs between the ages of 20 and 40. Moreover, individuals with a family history of autoimmune disorders may face a greater risk. Additionally, exposure to environmental triggers, such as UV light, certain medications, or infections, can further increase susceptibility.
Common Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Symptoms
The condition can manifest in several different forms, each presenting unique characteristics. Symptoms of cutaneous lupus may include:
- Red, scaly patches or plaques on the skin.
- Sensitivity to sunlight leading to flare-ups.
- Lesions that may cause scarring or discoloration.
- Inflammation on the scalp, which may result in hair loss.
- Itching, burning, or tenderness in affected areas.
Importantly, the severity of symptoms varies from person to person. While some may experience mild rashes that respond well to treatment, others may struggle with more persistent or scarring lesions. Therefore, recognizing these early signs is crucial for seeking timely medical care.
Types of Cutaneous Lupus
- Acute Cutaneous Lupus – Often associated with systemic lupus, this form presents as a butterfly-shaped rash across the cheeks and nose.
- Subacute Cutaneous Lupus – Characterized by red, scaly patches that may worsen with sun exposure, this subtype is less likely to cause scarring.
- Chronic Cutaneous Lupus (Discoid Lupus) – Perhaps the most common form, discoid lupus causes round, disc-shaped lesions that may result in permanent scarring or pigmentation changes.
Understanding the subtype is essential because it influences both prognosis and management strategies.
Emotional and Social Impact
Not only does this condition affect the skin, but it also has psychological implications. For instance, patients may feel self-conscious about visible rashes, leading to social withdrawal or anxiety. In addition, uncertainty about flare-ups can make daily planning stressful. Consequently, mental health support, such as counseling or support groups, can be just as important as medical treatment.
Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Treatment Options
Treatment typically involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, medications, and preventive strategies. Some common approaches include:
- Sun protection: Since UV rays are a major trigger, patients are advised to wear sunscreen daily, avoid peak sunlight hours, and use protective clothing.
- Topical treatments: Corticosteroid creams or ointments may help reduce inflammation in localized areas.
- Systemic medications: For more severe cases, physicians may prescribe antimalarial drugs (such as hydroxychloroquine) or immunosuppressive medications.
- Lifestyle changes: Quitting smoking, reducing stress, and following a balanced diet can support overall immune function.
Diagnosis and Testing
Typically, dermatologists conduct a thorough skin examination and may perform a biopsy to confirm the condition. Furthermore, blood tests may help rule out systemic lupus or identify markers of autoimmune activity. Early diagnosis not only clarifies the type of lupus present but also guides more effective treatment choices.
Living with Cutaneous Lupus
Day-to-day management is crucial. Because flare-ups can be unpredictable, patients often benefit from adopting consistent routines. For instance, maintaining a skincare regimen with gentle, fragrance-free products can reduce irritation. Additionally, keeping a symptom diary may help identify triggers, such as specific foods, medications, or levels of sun exposure.
Moreover, patients should not underestimate the value of community support. Joining patient advocacy groups or online forums can provide encouragement, practical tips, and reassurance that they are not facing this challenge alone.
Advances in Research
Encouragingly, medical research continues to make progress in understanding cutaneous lupus erythematosus. For example, scientists are investigating how genetics, hormones, and environmental triggers interact to spark immune dysfunction. At the same time, clinical trials are testing new biologic therapies designed to target specific immune pathways. As these innovations evolve, patients may gain access to more personalized and effective treatments in the future.
Preventive Strategies
- Applying broad-spectrum sunscreen with high SPF daily.
- Wearing wide-brimmed hats and protective clothing outdoors.
- Staying hydrated and nourishing the body with anti-inflammatory foods.
- Regularly following up with healthcare providers to adjust treatment as needed.
Although these steps may seem simple, they can make a significant difference in reducing the frequency and severity of flare-ups.
Final Thoughts
Cutaneous lupus erythematosus is a complex autoimmune skin disorder that can profoundly impact physical, emotional, and social well-being. While it is not typically life-threatening, its visible symptoms and chronic nature demand both medical attention and emotional resilience. Fortunately, through a combination of sun protection, medications, lifestyle modifications, and supportive care, many patients are able to manage their condition effectively.
As we have discussed, knowing the cutaneous lupus erythematosus symptoms allows for early detection. Additionally, cutaneous lupus treatment options empower patients to take an active role in their care. Moreover, ongoing research continues to provide hope for even better therapies in the future. Above all, it is essential to remember that no one is alone in this journey. With the right combination of medical care, preventive strategies, and emotional support, living with cutaneous lupus can become a more manageable experience.
Need support for your clinical trials?
Your journey to better care starts here, reach out to us today!
