Last Updated on August 22, 2025
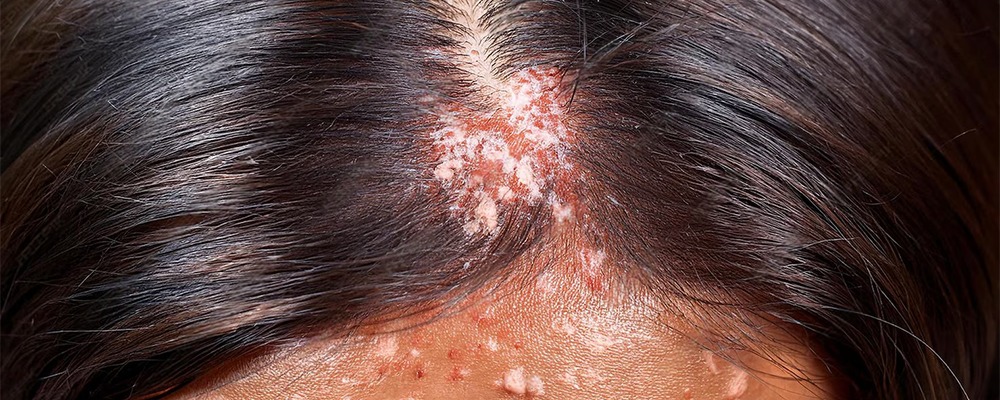
Scalp eczema is more common and often begins in infancy, while scalp psoriasis usually appears between ages 15 and 35. Eczema on the scalp is usually very itchy with dry, flaky skin, whereas psoriasis often causes thick, clearly defined patches that may sting or burn.
While neither condition has a cure, various treatment strategies and lifestyle changes can help manage symptoms. However, what works for eczema may not work for psoriasis. So, it’s important to see a dermatologist for an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan.
Read more to learn more about the similarities and differences between scalp eczema and psoriasis, how they are diagnosed, and how you can manage them better.
What Is Scalp Eczema?
Scalp eczema, also called seborrheic dermatitis, is a skin condition that primarily affects areas of the scalp that are rich in oil-producing (sebaceous) glands and causes inflammation, redness, and greasy, yellowish flakes. It often feels itchy and may get worse in cold weather or with stress.
To learn more, participate in our clinical trials for eczema.
What Is Scalp Psoriasis?
Scalp psoriasis is an autoimmune skin disorder that causes your skin cells to grow too fast, leading to thick, silvery-white scales and red patches all over the scalp. It can also extend behind the ears and even along the hairline.
To learn more about scalp psoriasis, take part in our ongoing psoriasis clinical trials.
Scalp Eczema vs Psoriasis: Differences
Even though both conditions affect the scalp, they still differ in the following ways:
-
Appearance:
Scalp eczema looks greasy and flaky, while psoriasis has thicker, rough, silvery-white scales.
-
Cause:
Eczema is often caused by overactive oil glands or a reaction to weather, stress, or allergens. Whereas psoriasis is an autoimmune condition and is often linked to family history.
-
Location on the Scalp:
Eczema usually stays limited to the scalp, while scalp psoriasis can extend beyond it, affecting areas like the neck or ears (psoriasis in ears).
Scalp Eczema vs Psoriasis: Similarities
Both scalp eczema and scalp psoriasis are very different from each other, yet share some common, overlapping symptoms. They include:
- Both conditions cause significant scalp itching that can interfere with daily activities and sleep.
- Both produce visible flakes and scales, though they differ in appearance.
- Inflammation and redness are present in both conditions.
- Both may come and go in flare-ups, especially in cold or dry weather.
- Both conditions may feel worse with stress, certain hair products, or poor scalp hygiene.
- Severe cases of either condition can lead to temporary hair thinning.
- There is no cure for either scalp eczema or scalp psoriasis, but treatments can help manage symptoms.
Scalp Eczema vs Psoriasis: Causes
Both scalp eczema and scalp psoriasis are linked to problems with how the immune system works.
Scalp Eczema Causes
Scalp eczema often happens when the immune system overreacts to certain triggers from inside or outside the body.
Research shows that some people may have a gene change that makes their skin more prone to dryness, allergies, and irritation.
Common triggers for scalp eczema flare-ups include:
- Stress
- Hormonal changes
- Weather changes
- Certain medications
- Health conditions like HIV or Parkinson’s disease
- Fragrances, detergents, and skin care products
- Contact with materials such as nickel or latex
- Harsh chemicals
Read more: Is Eczema An Autoimmune Disease or Something Else?
Scalp Psoriasis Causes
Scalp psoriasis develops when the immune system sends the wrong signals, making skin cells grow too quickly. Because the body can’t shed these extra cells fast enough, they build up on the scalp, forming thick patches.
Common triggers for scalp psoriasis include:
- Infections such as strep throat or HIV
- Certain medications
- Stress
- Smoking
- Obesity
- Sunburn
- Heavy alcohol use
- Family history of psoriasis
Scalp Eczema vs Psoriasis: Diagnosis and Treatment
If you are unsure whether you have scalp eczema or psoriasis, it’s important to see a dermatologist. They may use the following approaches to diagnose your condition:
- Physical Examination: Visual inspection of affected areas
- Medical History: Discussion of symptoms, family history, and triggers
- Dermoscopy: Magnified examination of the scalp and skin
- Skin Biopsy: In rare cases, a small tissue sample may be taken for analysis
While treatment should always be guided by a healthcare professional, understanding general approaches can help you make informed decisions about your care.
Scalp Eczema Treatment:
- Medicated Shampoos: Containing ketoconazole, selenium sulfide, or zinc pyrithione
- Topical Antifungals: To address yeast overgrowth
- Gentle Hair Care: Using mild, fragrance-free products
- Stress Management: Techniques to reduce stress-related flare-ups
Scalp Psoriasis Treatment:
- Prescription Shampoos: With coal tar or salicylic acid
- Topical Corticosteroids: To reduce inflammation
- Vitamin D Analogues: Such as calcipotriene
- Systemic Treatments: For severe cases, including biologics or immunosuppressants
NOTE: Always follow your doctor’s advice and never scratch the affected area, as it can make things worse.
When to Seek Medical Attention:
- Persistent symptoms lasting more than a few weeks
- Severe itching that interferes with daily activities
- Signs of infection (increased redness, warmth, pus, or fever)
- Symptoms that don’t respond to over-the-counter treatments
- Symptoms that significantly impact your quality of life
- Hair loss or thinning
Also read: The Connection Between Seborrheic Dermatitis and Hair Loss
Scalp Eczema vs Psoriasis: Prevention and Management Tips
Regardless of which condition you have, certain lifestyle modifications can help manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups:
General Care Tips:
- Gentle Hair Care: Use mild, sulfate-free shampoos and avoid harsh chemicals
- Stress Management: Practice relaxation techniques, exercise, or meditation
- Avoid Triggers: Identify and minimize exposure to personal triggers
- Maintain Scalp Hygiene: Regular, gentle cleansing without over-washing
- Protect from Weather: Use appropriate head covering in extreme weather
- Healthy Diet: Some people find that certain dietary changes help manage symptoms
Long-term Management:
Both conditions need consistent, long-term care. Therefore, the best results come from working closely with a dermatologist to create a treatment plan customized to your needs, while also taking part in ongoing research. There are several benefits of participating in clinical research. For example:
- Get access to new and promising treatments before they are available to the public.
- Receive expert medical care and close health monitoring from specialists.
- Contribute to advancing medical research and helping future patients.
Final Thoughts
While there are some similarities between scalp eczema and psoriasis, understanding their key differences is essential for proper treatment and management.
The differences between them lie primarily in their appearance, underlying causes, and treatment responses, while their similarities include common symptoms, diagnostic methods, and lifestyle changes.
Therefore, if you or someone you know is struggling with long-term scalp issues, speak to a doctor. They will help you provide the right diagnosis and treatment plans.
And lastly, if you’re interested in participating in research studies, now is a great time to explore safe, cutting-edge options at MBCP and create a healthier future for everyone.
Need support for your clinical trials?
Your journey to better care starts here, reach out to us today!
