Last Updated on August 13, 2025
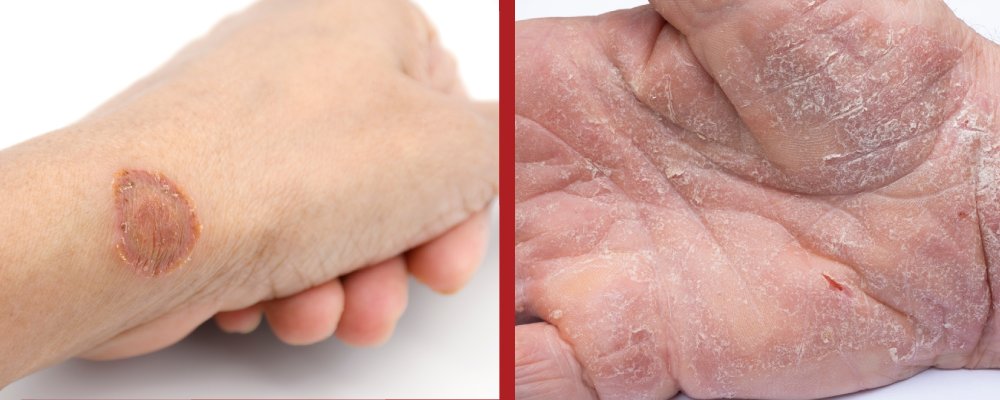
Skin conditions can be challenging to manage, especially when they appear similar. Two common conditions that often cause confusion are ringworm and eczema. Although both affect the skin, they have different causes, symptoms, and treatment options. Being able to recognize the differences is essential for proper care and faster recovery. In this blog, we’ll explore the signs, causes, and treatment options for ringworm vs eczema, helping you understand how to differentiate and manage these conditions effectively.
What is a Ringworm?
Ringworm, also called tinea, is a fungal infection that targets the skin. It gets its name from the red, circular rash it often causes, which can resemble a ring. Unlike eczema, ringworm is caused by fungi that live on the skin’s surface. The most common areas affected by this infection include the scalp, body, feet (athlete’s foot), and groin (jock itch).
Ringworm spreads easily through direct contact with infected individuals, animals, or contaminated objects such as towels and clothing. In the context of ringworm vs eczema, understanding how contagious ringworm is makes early treatment crucial to prevent spreading.
What is Eczema?
Eczema, or atopic dermatitis, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that causes dry, itchy, and irritated patches on the skin. Unlike ringworm, eczema is not caused by an infection but by a combination of genetic factors, immune responses, and environmental triggers. This condition is often hereditary, and people with allergies or asthma are more prone to developing it.
Eczema commonly affects areas like the face, hands, elbows, and knees. Moreover, various factors can trigger eczema flare-ups, including stress, exposure to irritants like harsh soaps, and changes in weather. Managing eczema involves avoiding triggers including eczema bumps on the elbows, and maintaining proper skin hydration.
Key Differences Between Ringworm and Eczema
Appearance
When comparing ringworm vs eczema, several important differences become evident that can significantly impact diagnosis and treatment. Ringworm presents as red, circular, and scaly patches with raised borders, creating a distinct ring-like appearance. This visual characteristic is particularly helpful in identifying the condition.
In contrast, eczema manifests as dry, itchy, red patches that can occur in various shapes and sizes. These patches often lack a defined border and can be uneven in texture, making them less distinctive than ringworm.
Itchiness and Discomfort
Next, consider itchiness and discomfort. With ringworm, individuals typically experience mild to moderate itching, which may worsen as the infection spreads. The affected areas can become more irritated and uncomfortable over time.
Conversely, eczema often causes intense itching that can be debilitating. This itching frequently intensifies in response to environmental triggers or stress, leading to a cycle of scratching and irritation that can exacerbate the condition.
Cause
The cause of each condition also plays a significant role in their differences. Ringworm is caused by a fungal infection, which means it requires antifungal treatments to eliminate the underlying organism.
In contrast, eczema is classified as an inflammatory skin condition that arises from a combination of genetic predisposition, immune system response, and environmental factors. As a result, eczema is often managed through moisturization, corticosteroids, and lifestyle adjustments rather than antifungal medications.
Note: For insights on whether Is Eczema An Autoimmune Disease or Something Else? be sure to read our blog.
Contagion
Finally, consider contagion. ringworm is highly contagious and spreads easily through direct contact with an infected person, animal, or contaminated objects, such as towels or clothing. This high level of contagion necessitates quick intervention to prevent spreading the infection to others.
On the other hand, eczema is non-contagious; it cannot be spread from person to person. This distinction alleviates concerns about contagion for those dealing with eczema, allowing individuals to focus on managing their symptoms effectively without fear of transmitting the condition to others.
How to Diagnose Ringworm and Eczema
Diagnosing ringworm vs eczema requires a thorough medical evaluation. Doctors begin with a physical examination and a detailed review of your medical history. They will look at the appearance of the rash and ask questions about your symptoms, potential exposure to infectious sources, and any family history of skin conditions or allergies.
To confirm ringworm, a skin scraping test is often performed. This involves gently scraping off a small part of the affected skin, which is then examined under a microscope or sent to a lab for fungal culture. This test helps identify whether a fungal infection is present.
For eczema, doctors commonly use patch testing to detect allergic reactions that may cause or worsen the condition. Small amounts of various substances are applied to your skin to see if any of them cause a reaction, helping to identify specific allergens or irritants responsible for eczema flare-ups.
Timely diagnosis and proper treatment can prevent complications and improve skin health.
Treatment and Management
When dealing with ringworm vs eczema, the treatment approaches differ significantly due to the distinct causes of each condition.
For ringworm, the first line of treatment is often over-the-counter antifungal creams. These creams help eliminate fungal infection and relieve symptoms. In more severe cases, doctors may prescribe oral antifungal medications to fully treat the infection. Additionally, maintaining good hygiene is essential to prevent the spread of ringworm. This includes regularly washing hands, keeping the affected area clean and dry, and avoiding sharing personal items like towels or clothing.
In contrast, treating eczema focuses on managing the symptoms and reducing flare-ups. Regular use of moisturizers and emollients helps keep the skin hydrated, which is key to minimizing irritation and itching. Doctors may also prescribe topical corticosteroids or other prescription medications to control inflammation. Beyond medication, lifestyle modifications are critical. Avoiding triggers such as harsh soaps, allergens, or stress, and using gentle skin care products can significantly reduce the frequency of eczema flare-ups.
In cases where eczema becomes more severe or persistent, advanced treatment options like light therapy may be recommended. This therapy uses ultraviolet light to reduce inflammation and improve skin condition.
If either condition persists despite treatment, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider for further evaluation and stronger interventions.
Preventing Recurrence
Preventing the recurrence of ringworm vs eczema involves different strategies tailored to the nature of each condition.
For ringworms, maintaining proper hygiene and cleanliness is crucial. Regularly washing your hands and body can help reduce the risk of reinfection. Additionally, it’s important to avoid sharing personal items such as towels, clothing, or grooming tools with others, as this can easily spread the infection. If pets are infected, they should also be treated to prevent the fungus passing back to humans.
On the other hand, for eczema, prevention focuses on keeping the skin healthy and avoiding triggers. A consistent moisturizing routine is essential to maintain the skin’s protective barrier and prevent dryness that can lead to flare-ups. It’s equally important to avoid known triggers. Managing stress and maintaining a balanced diet can also play a key role in minimizing eczema flare-ups, as both factors can influence the severity of the condition.
By following these preventive measures, you can reduce the chances of experiencing recurrent symptoms of both ringworm and eczema.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the differences between ringworm vs. eczema is key to proper diagnosis and treatment. While both conditions affect the skin, ringworm is a fungal infection, whereas eczema is an inflammatory skin condition. Recognizing whether you have ringworm or eczema allows for more effective management. With ringworm, antifungal treatments and good hygiene are crucial, while eczema requires moisturizers, avoiding triggers, and managing stress. By identifying the right condition, whether it’s ringworm vs. eczema, you can take the appropriate steps to treat it and prevent recurrence, ensuring healthier skin in the long run.
