Last Updated on August 13, 2025
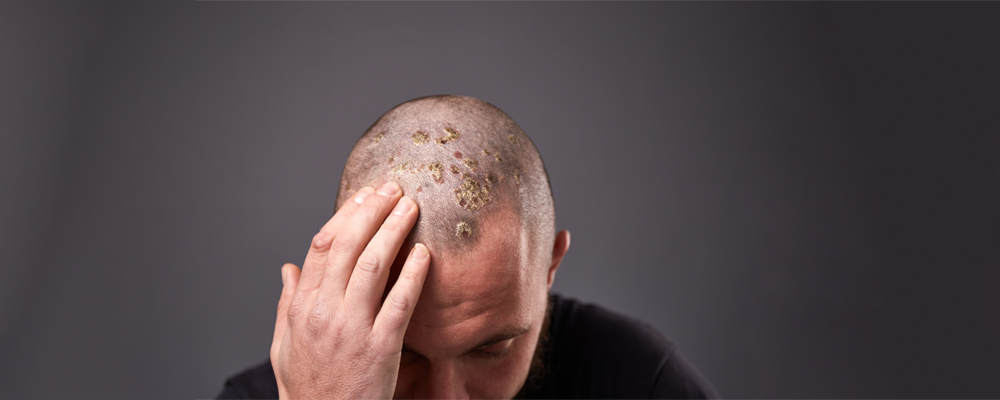
Scalp eczema is also known as seborrheic dermatitis. It is a common inflammatory skin condition that affects the scalp. Additionally, it can cause redness, itching, and flaky patches on the skin, leading to discomfort and embarrassment. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for managing this condition effectively.
Causes of Scalp Eczema
It is caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some of the primary causes include genetics, a family history of eczema or other inflammatory skin conditions which can increase the likelihood of developing scalp eczema. The naturally occurring Malassezia yeast on the skin can sometimes overgrow, leading to an inflammatory response and triggering eczema symptoms.
Furthermore, an overactive immune system can respond to harmless substances as if they were harmful, causing inflammation and eczema flare-ups. Additionally, cold weather, low humidity, harsh hair products, and stress can exacerbate the symptoms. Hormonal fluctuations, such as those experienced during puberty or pregnancy, can trigger or worsen it.
Symptoms of Scalp Eczema
The symptoms can vary in severity and may include redness and inflammation, with the scalp appearing red and inflamed, often accompanied by itching. White or yellowish flakes can form on the scalp, resembling dandruff but more persistent. Furthermore, intense itching is a common symptom, leading to scratching that can worsen the condition and cause secondary infections.
In some cases, the scalp may become greasy due to increased sebum production, which can exacerbate the condition. Severe cases may result in crusty patches and weeping sores on the scalp.
How Is Scalp Eczema Diagnosed?
Diagnosing scalp eczema requires a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare provider, typically a dermatologist, who specializes in skin conditions. The process begins with a detailed examination of the scalp’s appearance, noting characteristics such as redness, flaking, and inflammation. Furthermore, the dermatologist will also review the patient’s medical history to identify any underlying factors or previous skin conditions that might contribute to the symptoms.
During the consultation, the healthcare provider may ask about the patient’s symptoms, such as itching, pain, or the presence of crusty patches. They might inquire about any family history of eczema or other inflammatory skin conditions, as these can increase the likelihood of developing it. Additionally, questions about lifestyle, stress levels, and recent changes in hair care products can help pinpoint potential triggers.
However, in some cases, to ensure an accurate diagnosis and rule out other conditions that resemble scalp eczema, a skin biopsy may be performed. This involves removing a small sample of skin from the affected area, which is then examined under a microscope.
What are Similar Conditions to Scalp Eczema?
This condition shares symptoms with other conditions, making accurate diagnosis crucial. Some similar conditions include:
- Psoriasis: This condition also causes red, scaly patches but often has thicker scales and may affect other areas of the body, like the elbows and knees.
- Contact Dermatitis: This type of eczema results from an allergic reaction to substances like hair dyes or shampoos.
- Tinea Capitis: A fungal infection of the scalp, tinea capitis, can cause itching and flaking but typically presents with broken hairs and round patches of hair loss.
- Dandruff: While dandruff causes flaking, it usually lacks inflammation and redness.
Treatment for Scalp Eczema
Moreover, effective management of scalp eczema involves a combination of medical treatments, lifestyle changes, and home care practices. Here are some common treatment options:
Medications
- Topical Steroids: These are often prescribed to reduce inflammation and itching. They come in various strengths and are applied directly to the affected areas.
- Antifungal Treatments: If Malassezia yeast is contributing to the condition, antifungal shampoos or creams can help control its growth.
- Calcineurin Inhibitors: These non-steroidal medications can reduce inflammation and are suitable for long-term use in sensitive areas like the scalp.
- Oral Medications: In severe cases, oral medications such as antifungals or immunosuppressants may be prescribed.
Home Care and Lifestyle Changes
- Gentle Hair Care: Use mild, fragrance-free shampoos and conditioners. Avoid harsh hair treatments and minimize the use of styling products that can irritate the scalp.
- Moisturize: Regularly moisturizing the scalp can help reduce dryness and flaking. Look for products specifically designed for sensitive skin.
- Stress Management: Stress can trigger or worsen eczema flare-ups. Techniques like meditation, yoga, and deep-breathing exercises can help manage stress levels.
- Balanced Diet: A diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids, can support overall skin health.
- Avoid Triggers: Identify and avoid environmental triggers, such as cold weather, harsh hair products, and allergens, that can exacerbate symptoms.
Natural Remedies
Some natural remedies may help alleviate the symptoms. While these should not replace medical treatments, they can be used as complementary approaches. Tea tree oil, known for its antifungal and anti-inflammatory properties, can be added to shampoo or diluted with carrier oil and applied to the scalp.
Additionally, aloe vera gel can soothe irritated skin and reduce inflammation; apply it directly to the affected areas for relief. Coconut oil can moisturize the scalp and reduce flaking. Apply it to the scalp and leave it on for a few hours before washing it off. Furthermore, diluted apple cider vinegar can help balance the scalp’s pH and reduce yeast overgrowth. Rinse the scalp with a mixture of water and apple cider vinegar after shampooing.
When to See a Doctor?
While many cases of scalp eczema can be managed with over-the-counter treatments and home care, it’s important to seek medical advice if symptoms worsen or do not improve with treatment. Moreover, if the condition spreads beyond the scalp, or if you experience severe itching, pain, or signs of infection, such as pus or oozing sores.
Furthermore, mild symptoms might respond well to regular use of medicated shampoos containing ingredients like ketoconazole, selenium sulfide, or zinc pyrithione. These shampoos can help reduce inflammation and control the growth of yeast that can exacerbate eczema.
However, if the condition does not improve with these measures, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider. Persistent or severe symptoms might indicate a need for stronger treatments or a more comprehensive approach. For example, prescription-strength topical corticosteroids or antifungal medications might be necessary to control inflammation and infection effectively.
Conclusion
It is a manageable condition with the right approach. By understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and seeking appropriate treatment, individuals can effectively control and minimize flare-ups. Furthermore, you can also look for other treatment options like clinical trials and get relief. If you suspect you have scalp eczema, consult a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
